The air conditioning system maintains temperature, humidity and air quality parameters within comfortable conditions, promoting savings in the building’s energy consumption.
The air conditioning system maintains temperature, humidity and air quality parameters within comfortable conditions, promoting savings in the building’s energy consumption.
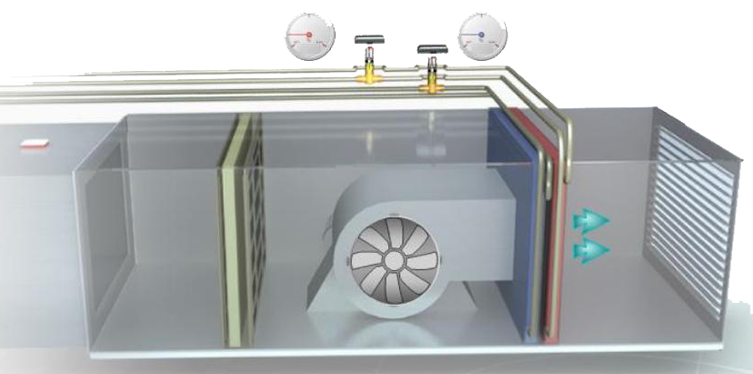
- Production of cold and heat
- Accumulation of cold or hot water.
- Pump regulation for flow distribution
- Control of terminal units: fan coils, variable air volume boxes, air conditioners…
This energy saving management can be structured in a series of good practices implemented and tested by Vereda System Sotecontrol such as those detailed below:
- Zone programming; ; permite tener zonas definidas en un edificio con niveles de climatización según un calendario, adaptando las distintas zonas a sus necesidades reales según la ocupación del momento, sin tener la necesidad de mantener toda la instalación al 100%
- Occupancy control: In this application, the HVAC comfort setpoints are changed such that the room temperature decreases in winter and increases in summer, reducing the demand for cooling and heating during the hours when the room is not occupied.
- Holiday and vacation scheduling; a calendar defines the control of offices, laboratories, consultation rooms, etc. for an entire year, saving staff time by implementing special schedules and ensuring that the system does not operate in busy mode during vacations, holidays, or weekends.
- Temporary after-hours settings; allows for changes to comfort settings after hours, eliminating the need to temporarily modify schedules that can accidentally become permanent. It also avoids having a zone in occupied mode to meet the needs of a small group.
- Optimal start and stop: The HVAC system is started only when it is required to bring the building to the required comfort level setpoints. The stop is determined at the optimal time to initiate the return of temperatures before periods of non-occupancy while maintaining comfort. Control routines take into account the outside air temperature when initiating morning cooling cycles.
- Demand ventilation; CO2 levels in a space are used as an indicator of room occupancy. This level is linked to the “fresh air” intake damper, indicating when a higher level of outside air is required.
- Optimization of heating and cooling production centers; the parameters of the production centers can be recalculated according to the load and needs of the building.
- DHW temperature adjustment; The DHW temperature can be adjusted based on the outside temperature, reducing heat losses in supply pipes.
- Variable speed drives; control over variable speed drives optimizes the energy consumption of the fans.